I. The Basic Principles and Characteristics of Nano-Sintered Silver
1.1 Definition
Nano-sintered silver refers to the formation of a silver layer with high electrical conductivity and high thermal conductivity through the sintering of nano-sized silver particles at an appropriate temperature. Compared with traditional silver materials, nano-silver particles, due to their size effect and surface effect, have a lower sintering temperature and better sintering performance. This enables nano-sintered silver to have broad application prospects in fields such as electronic packaging, conductive adhesives, and heat dissipation materials.
1.2 Characteristics of Nano-Sintered Silver
High Electrical Conductivity: The silver layer formed after the sintering of nano-sintered silver has electrical conductivity close to that of pure silver, which is suitable for the interconnection of high-performance electronic devices and the application of conductive adhesives.
High Thermal Conductivity: The silver layer formed after the sintering of nano-silver particles has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps to improve the heat dissipation efficiency of electronic devices and extend the service life of the devices.
Low Sintering Temperature: Due to their high surface energy, nano-silver particles can complete the sintering process at a relatively low temperature, which is suitable for temperature-sensitive electronic packaging processes.
Excellent Mechanical Properties: The silver layer formed after the sintering of nano-sintered silver has good mechanical strength and toughness and can withstand the stress and deformation generated during the electronic packaging process.
II. Preparation Methods of Nano-Sintered Silver
2.1 Preparation of Nano-Silver Particles
Chemical Reduction Method: Silver ions in silver salt solutions are reduced into silver particles by chemical reducing agents. This method is simple to operate and has a low cost, but it is difficult to precisely control the particle size and morphology.
Physical Evaporation Method: Silver metal is heated and evaporated and then condensed into nano-particles. The silver particles prepared by this method have high purity and uniform size, but the cost is relatively high and the equipment requirements are also high.
Sol-Gel Method: Silver nano-particles are formed through the sol-gel process. The particles prepared by this method have controllable size and uniform morphology, but it requires a complex chemical treatment process.
2.2 Preparation of Nano-Sintered Silver Paste
Silver Paste Preparation: Nano-silver particles are dispersed in organic solvents, and appropriate amounts of dispersants, binders and other functional additives are added to prepare a uniform nano-silver paste.
Paste Adjustment: By adjusting the concentration of nano-silver particles, the ratio of dispersants and binders, as well as the viscosity and rheological properties of the paste, the performance of the nano-silver paste is optimized to meet different application requirements.
2.3 Coating and Sintering of Nano-Silver Paste
In practical applications, nano-silver paste usually needs to be coated on the surface of substrates or devices and then sintered to form conductive or heat-conductive layers. Common coating methods include:
Screen Printing: Nano-silver paste is coated on the surface of the substrate by screen printing. This method is suitable for large-area coating and mass production.
Spraying: Nano-silver paste is evenly sprayed on the surface of the substrate through spraying equipment. This method is suitable for coating substrates with complex shapes.
Coating: Nano-silver paste is coated on the surface of the substrate by dip coating or spin coating. This method is suitable for small-area coating and laboratory preparation.
The sintering process is usually carried out at a relatively low temperature (150 °C - 300 °C) to avoid thermal damage to the substrate materials. The sintered silver layer has high electrical conductivity and high thermal conductivity and can be used for the interconnection and heat dissipation of electronic devices.
III. Applications of Nano-Sintered Silver in Electronic Packaging
3.1 Interconnection Materials in Electronic Packaging
In the field of electronic packaging, nano-sintered silver is widely used for the interconnection between chips and substrates. Traditional interconnection materials (such as lead-tin solders, copper) have problems such as insufficient electrical conductivity, poor thermal conductivity and environmental protection issues. While nano-sintered silver, due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, has become an ideal alternative to traditional materials.
3.2 Applications in High-Power Electronic Devices
High-power electronic devices (such as power semiconductors, LED) have extremely high requirements for heat dissipation performance. Nano-sintered silver, due to its excellent thermal conductivity, can be used as an ideal heat dissipation material to improve the heat dissipation efficiency of devices and extend the service life of the devices. In addition, nano-sintered silver also has a low thermal expansion coefficient, which can effectively reduce the stress and deformation caused by thermal expansion and improve the reliability of the devices.
3.3 Applications in Flexible Electronic Devices
With the development of flexible electronics technology, flexible electronic devices have put forward higher requirements for the flexibility and reliability of interconnection materials. Nano-sintered silver, due to its good mechanical properties and processability, can be applied to the interconnection and conductive lines of flexible electronic devices to meet the special needs of flexible electronic devices.


 PA-100A03B Chip-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature chip-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 230°C. Compared to traditional solders, this product offers a 5x improvement in thermal conductivity and extends service life by more than 10 times. Utilizing a printing process, it is suitable for connections between power chips and substrates, ensuring higher thermal conductivity and reliability in applications.
PA-100A03B Chip-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature chip-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 230°C. Compared to traditional solders, this product offers a 5x improvement in thermal conductivity and extends service life by more than 10 times. Utilizing a printing process, it is suitable for connections between power chips and substrates, ensuring higher thermal conductivity and reliability in applications.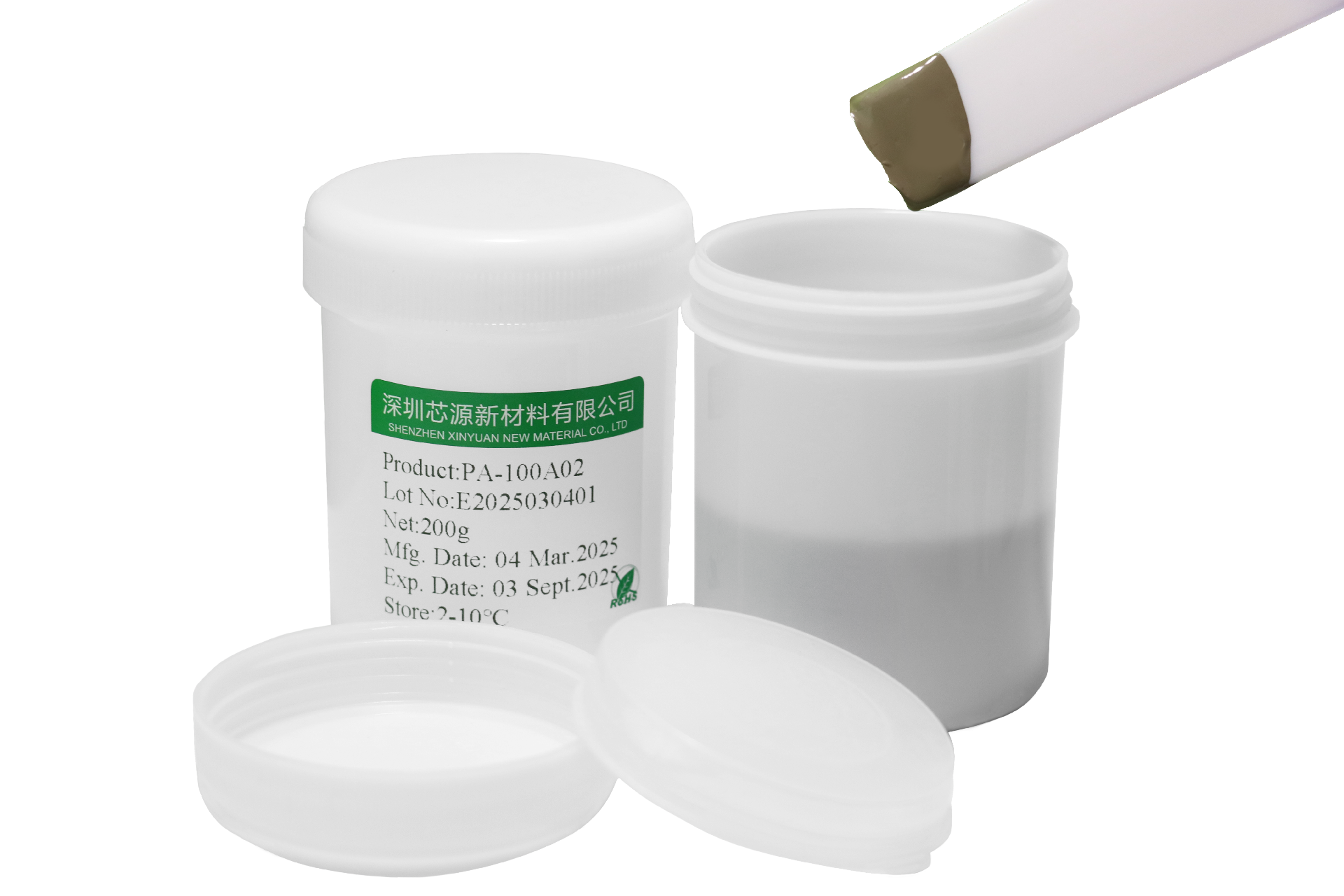 PA-100A02 Chip-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature chip-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 230°C. Compared to traditional solders, this product offers a 5x improvement in thermal conductivity and extends service life by more than 10 times. Utilizing a printing process, it is suitable for connections between power chips and substrates, ensuring higher thermal conductivity and reliability in applications.
PA-100A02 Chip-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature chip-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 230°C. Compared to traditional solders, this product offers a 5x improvement in thermal conductivity and extends service life by more than 10 times. Utilizing a printing process, it is suitable for connections between power chips and substrates, ensuring higher thermal conductivity and reliability in applications.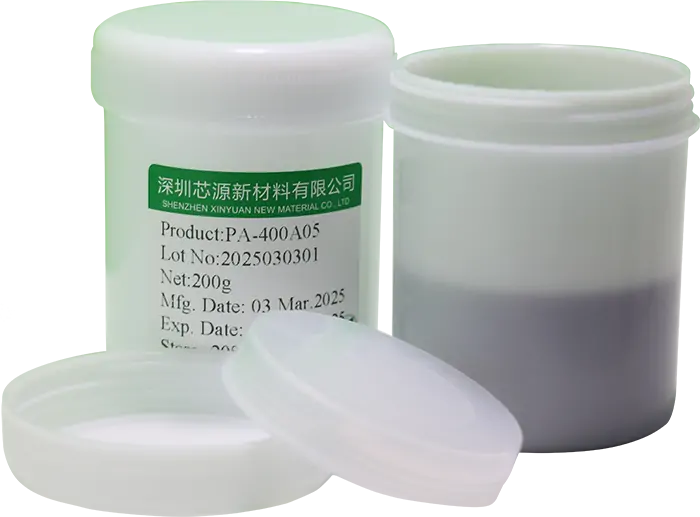 PA-400A05 System-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature system-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 200°C. Unlike chip-level pressure-assisted silver pastes, this system-level sintering silver paste enables large-area (≥2000 mm²) module packaging, offering significantly superior thermal performance and mechanical reliability compared to traditional solders.
PA-400A05 System-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature system-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 200°C. Unlike chip-level pressure-assisted silver pastes, this system-level sintering silver paste enables large-area (≥2000 mm²) module packaging, offering significantly superior thermal performance and mechanical reliability compared to traditional solders. PA-400A02A System-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature system-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 200°C. Unlike chip-level pressure-assisted silver pastes, this system-level sintering silver paste enables large-area (≥2000 mm²) module packaging, offering significantly superior thermal performance and mechanical reliability compared to traditional solders.
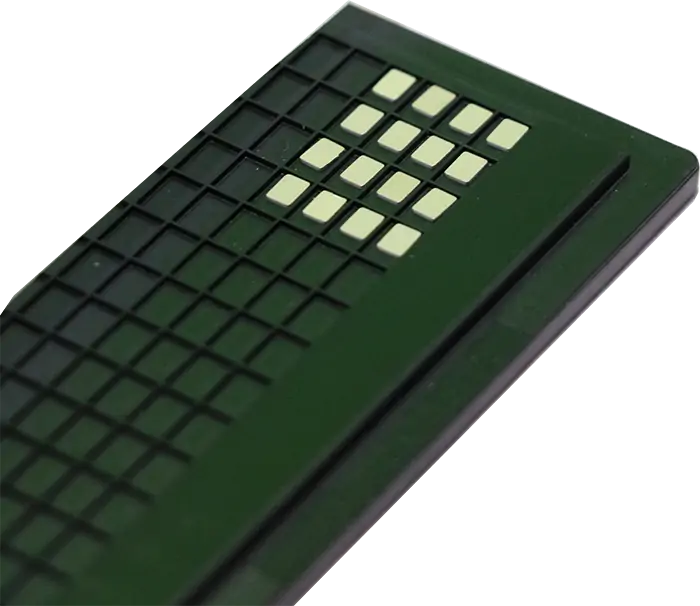
PA-400A02A System-level Sinter Silver PasteA silver paste capable of achieving low-temperature system-level interconnections, with a sintering temperature as low as 200°C. Unlike chip-level pressure-assisted silver pastes, this system-level sintering silver paste enables large-area (≥2000 mm²) module packaging, offering significantly superior thermal performance and mechanical reliability compared to traditional solders.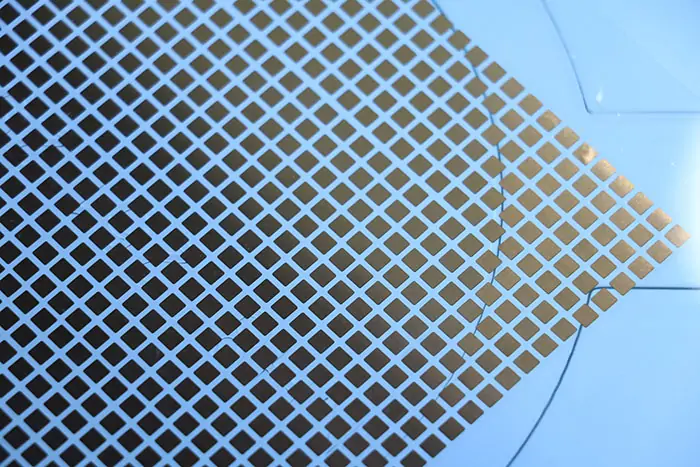 PA-300A01-50NP Sinter Copper ElectrodeAn electrode sheet capable of achieving top-side interconnections for chips, compatible with copper wire ultrasonic bonding for wire diameters of 300-400 μm. Compared to aluminum wire, copper wire offers superior mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and reliability, enabling higher current density and longer service life. This solution is suitable for SiC module and IGBT module packaging applications.
PA-300A01-50NP Sinter Copper ElectrodeAn electrode sheet capable of achieving top-side interconnections for chips, compatible with copper wire ultrasonic bonding for wire diameters of 300-400 μm. Compared to aluminum wire, copper wire offers superior mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and reliability, enabling higher current density and longer service life. This solution is suitable for SiC module and IGBT module packaging applications.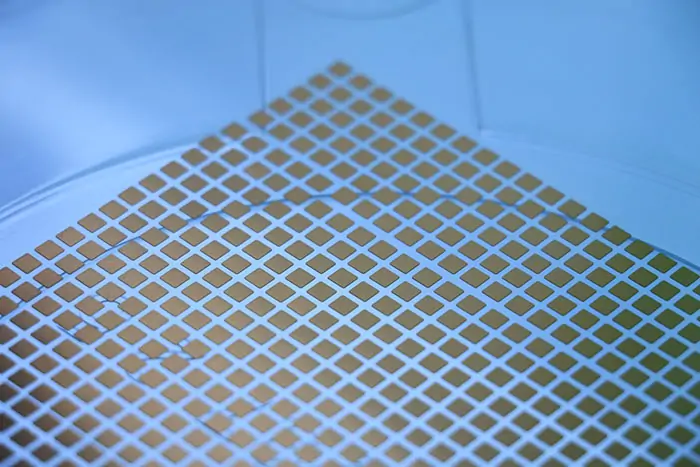 PA-300A03-507B Sinter Copper ElectrodeAn electrode sheet capable of achieving top-side interconnections for chips, compatible with copper wire ultrasonic bonding for wire diameters of 300-400 μm. Compared to aluminum wire, copper wire offers superior mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and reliability, enabling higher current density and longer service life. This solution is suitable for SiC module and IGBT module packaging applications.
PA-300A03-507B Sinter Copper ElectrodeAn electrode sheet capable of achieving top-side interconnections for chips, compatible with copper wire ultrasonic bonding for wire diameters of 300-400 μm. Compared to aluminum wire, copper wire offers superior mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and reliability, enabling higher current density and longer service life. This solution is suitable for SiC module and IGBT module packaging applications. PA-300A03-507A Sinter Copper ElectrodeAn electrode sheet capable of achieving top-side interconnections for chips, compatible with copper wire ultrasonic bonding for wire diameters of 300-400 μm. Compared to aluminum wire, copper wire offers superior mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and reliability, enabling higher current density and longer service life. This solution is suitable for SiC module and IGBT module packaging applications.
PA-300A03-507A Sinter Copper ElectrodeAn electrode sheet capable of achieving top-side interconnections for chips, compatible with copper wire ultrasonic bonding for wire diameters of 300-400 μm. Compared to aluminum wire, copper wire offers superior mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and reliability, enabling higher current density and longer service life. This solution is suitable for SiC module and IGBT module packaging applications. PA-600C01A System-level Sinter Copper PasteAn innovatively developed pressure-assisted sinter copper paste material, designed for reliable interconnections between chip/substrate and substrate/heat sink. It is compatible with the production processes and equipment used for sinter silver, while offering superior mechanical performance and cost advantages compared to silver paste. This makes it an ideal solution for high-power module packaging.
PA-600C01A System-level Sinter Copper PasteAn innovatively developed pressure-assisted sinter copper paste material, designed for reliable interconnections between chip/substrate and substrate/heat sink. It is compatible with the production processes and equipment used for sinter silver, while offering superior mechanical performance and cost advantages compared to silver paste. This makes it an ideal solution for high-power module packaging. PA-700C01A Chip-level Sinter Copper PasteAn innovatively developed pressure-assisted sinter copper paste material, designed for reliable interconnections between chip/substrate and substrate/heat sink. It is compatible with the production processes and equipment used for sinter silver, while offering superior mechanical performance and cost advantages compared to silver paste. This makes it an ideal solution for high-power module packaging.
PA-700C01A Chip-level Sinter Copper PasteAn innovatively developed pressure-assisted sinter copper paste material, designed for reliable interconnections between chip/substrate and substrate/heat sink. It is compatible with the production processes and equipment used for sinter silver, while offering superior mechanical performance and cost advantages compared to silver paste. This makes it an ideal solution for high-power module packaging.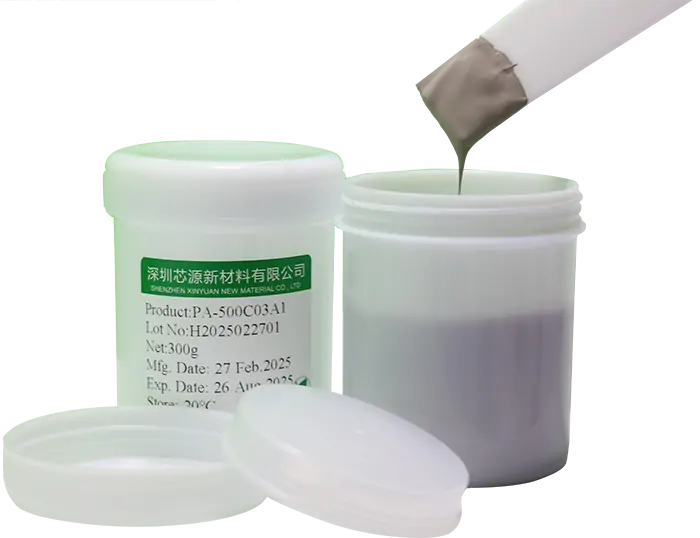 PA-500C03A1 Nano Copper Composite Solder (TLPS)A solder capable of achieving low-temperature, low-pressure interconnections, with a soldering temperature as low as 230°C. It is suitable for both large-area chip-level soldering and system-level module soldering, offering excellent mechanical strength and reliability.
PA-500C03A1 Nano Copper Composite Solder (TLPS)A solder capable of achieving low-temperature, low-pressure interconnections, with a soldering temperature as low as 230°C. It is suitable for both large-area chip-level soldering and system-level module soldering, offering excellent mechanical strength and reliability. PF-01A80 Pressureless Sinter Silver PasteHigh Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Sintered Conductive Silver Paste. Thermal conductivity up to 270 W/m·K, curing temperature 200℃.With exhibits stable and high bond strength on gold/silver interfaces.
PF-01A80 Pressureless Sinter Silver PasteHigh Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Sintered Conductive Silver Paste. Thermal conductivity up to 270 W/m·K, curing temperature 200℃.With exhibits stable and high bond strength on gold/silver interfaces.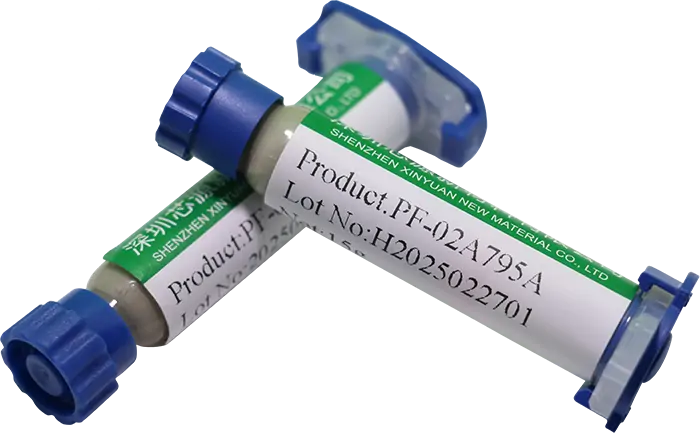 PF-02A795A Pressureless Sinter Silver PasteMedium to High Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Sintered Conductive Silver Paste with curing temperature 200℃. Outstanding continuous workability, wide process window, excellent thermal conductivity and reliability.
PF-02A795A Pressureless Sinter Silver PasteMedium to High Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Sintered Conductive Silver Paste with curing temperature 200℃. Outstanding continuous workability, wide process window, excellent thermal conductivity and reliability. PF-01B89SF6B Pressureless Semi-Sinter Silver AdhesiveMedium to High Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Semi-Sintered Conductive Adhesive. Enables interconnection of high stress mismatch structures and long-term service reliability.
PF-01B89SF6B Pressureless Semi-Sinter Silver AdhesiveMedium to High Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Semi-Sintered Conductive Adhesive. Enables interconnection of high stress mismatch structures and long-term service reliability. PF-01B91D Pressureless Sinter Silver AdhesiveMedium to High Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Semi-Sintered Conductive Adhesive with stable high bond strength on gold/silver interfaces. Particularly suitable for high-power and large-size LED packaging.
PF-01B91D Pressureless Sinter Silver AdhesiveMedium to High Thermal Conductivity Pressureless Semi-Sintered Conductive Adhesive with stable high bond strength on gold/silver interfaces. Particularly suitable for high-power and large-size LED packaging. PF-01B91C High Thermal Conductivity Conductive AdhesiveHigh Thermal Conductivity Conductive Adhesive with high thermal conductivity, long working time, 260℃ heat resistance. Suitable for medium to small power, high-reliability LED products.
PF-01B91C High Thermal Conductivity Conductive AdhesiveHigh Thermal Conductivity Conductive Adhesive with high thermal conductivity, long working time, 260℃ heat resistance. Suitable for medium to small power, high-reliability LED products. PF-03B85 High Temperature Resistance Conductive AdhesiveHigh Temperature Resistance Conductive Adhesive with strong dispensing stability, long working time, 260℃ heat resistance. Suitable for small-power LED products.
PF-03B85 High Temperature Resistance Conductive AdhesiveHigh Temperature Resistance Conductive Adhesive with strong dispensing stability, long working time, 260℃ heat resistance. Suitable for small-power LED products.